| Pay Percentages
Hourly
Rates
To make a fairer comparison we need to consider the distribution of pay rates, not ust the
average. The figures are given in Table 3.
| Rate |
Men % |
Women % |
| less than 60p |
0 |
0 |
| 60p to 79p |
0 |
3 |
| 80p to 99p |
1 |
10 |
| £1.00 to £1.19 |
4 |
20 |
| £1.20 to £1.39 |
11 |
22 |
| £1.49 to £1.59 |
15 |
15 |
| £1.60 to £1.79 |
15 |
10 |
| £1.80 to £1.99 |
13 |
6 |
| £2.00 to £2.39 |
17 |
6 |
| £2.40 to £2.99 |
12 |
4 |
| £3.00 to £3.99 |
8 |
3 |
| £4.00 and over |
4 |
1 |
(Source: New Earnings Survey)
Table - 3 Distribution of hourly earnings of workers in Britain, April 1978
Use Table 3 to answer these questions:
- What percentage of men earn £4.00 or more per hour? What percentage of women earn that
amount?
- What percentage of women earn less than £1.00 per hour? What percentage of men earn
that amount?
- What is the most common hourly pay rate for women? What is the most common hourly pay
rate for men?
- Write down two sentences comparing the hourly pay rates of men and women, as shown in
Table 3.
The
Cumulative Percentage Table
Fred says '70 per cent of female wage earners get paid less than £1.60 per hour.'
We use cumulative percentages to get these figures.
The column headed 'men' in Table 3 shows that:
None earn less than 80p per hour.
0 + 1 = 1 per cent earn less than £1.00 per hour.
1 + 4 = 5 per cent earn less than £1.20 per hour.
5 + 11 = 16 per cent earn less than £1.40 per hour.
- What percentage of men earn less than £1.60 per hour?
- What percentage of women earn less than £2.00per hour?
Table 4 shows some of these figures. We assume that no-one gets more than £5.00 per
hour.
- Look at the wage rates in Table 3. Do you think it is fair to assume that no-one gets
more than £5.00 per hour?
| Rates per hour |
Men (%) |
Women (%) |
| less than 60p |
0 |
0 |
| less than 80p |
0 |
3 |
| less than £1.00 |
1 |
13 |
| less than £1.20 |
5 |
|
| less than £1.40 |
16 |
|
| less than £1.60 |
|
|
| less than £1.80 |
|
|
| less than £2.00 |
|
|
| less than £2.40 |
|
|
| less than £3.00 |
|
|
| less than £4.00 |
|
|
| less than £5.00 |
|
|
Table 4 - Hourly pay rates for workers in Britain, April 19 78
(Cumulative percentages).
- Copy and complete Table 4. This is called a cumulative frequency table.
- What percentage of men earn £.20 per hour or more?
- What percentage of women earn £.00 per hour or more?
The
Cumulative Percentage Graph
One disadvantage of Table 4 is that it only gives some answers. We may want to know what
percentage of men earn less than £1.25. We may also want to know how much the lowest paid
25% of men earn and other similar questions. A graph like Figure 1 helps us estimate
answers to questions like these. The men's figures from Table 4 are shown in Figure 1.
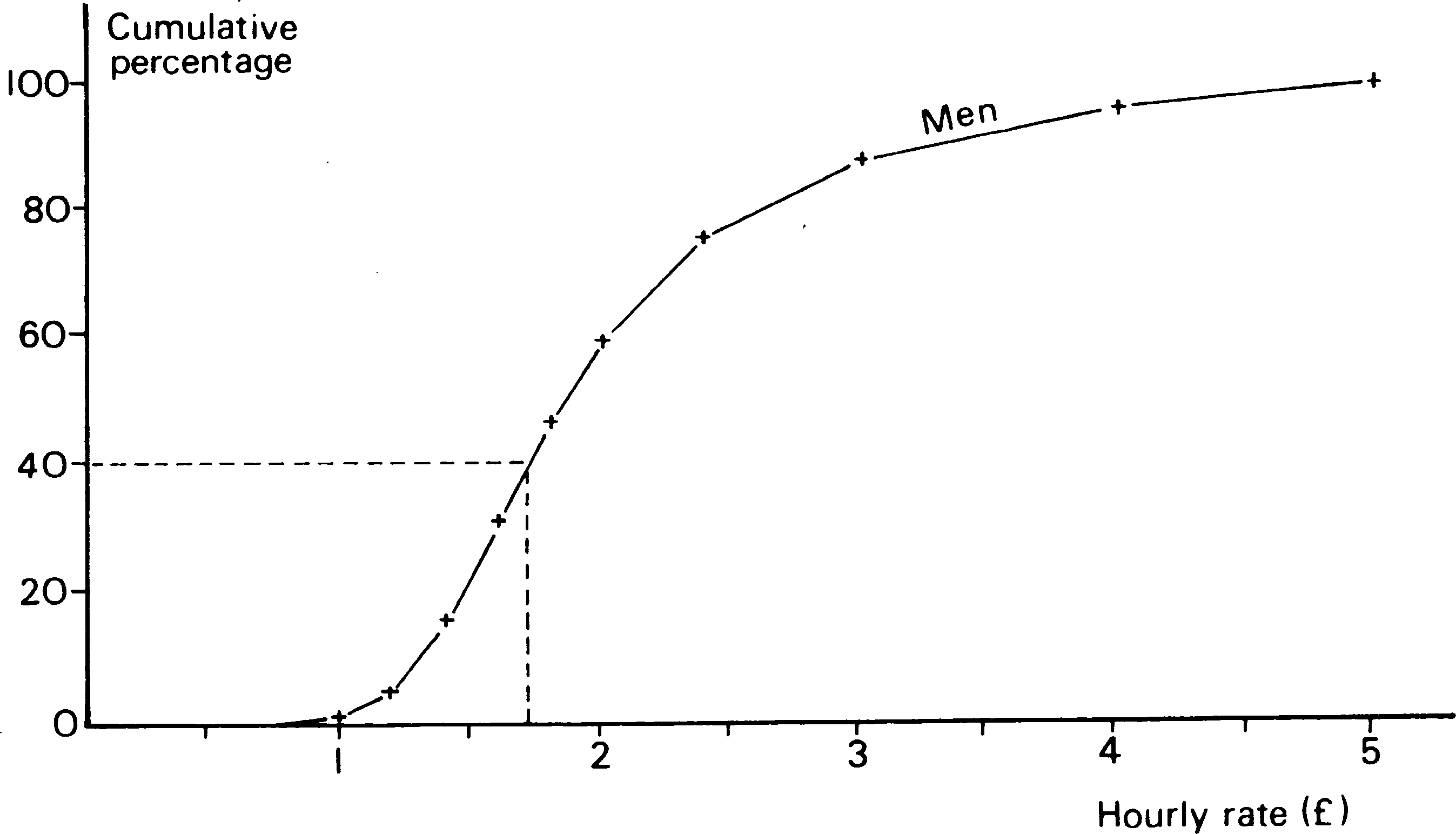
Figure 1 - Pay rates (April 1978)
Notice that the points are marked + These marks have been joined by straight lines.
- On a piece of graph paper use figures from your completed Table 4 to make your
own copy of Figure 1.
Plot the points for women's rates on the same graph.
Use a different coloured pencil to join these points with straight lines. Label this
'Women'.
On Figure 1a line has been drawn up f rom £1.75 to the men's graph. The line across
from here cuts the vertical axis at 40 per cent. This means that 40 per cent of the men
earn less than £1.75 per hour.
Use your graph to answer the following questions.
- What percentage of men earn less than £1.30 per hour?
- What percentage of women earn less than £1.30 per hour?
- What percentage of men earn less than £2.20 per hour?
- What percentage of women earn less than £2.20 per hour?
The Median
We are trying to compare men's and women's rates of pay. If we could find a 'middle' man
and a 'middle' woman, we could compare their wage rates.
Alan earns £1.86 per hour.
From your cumulative percentage graph:
- Find the percentage of men who earn less than Alan.
- Find the percentage of men who earn more than Alan.

We can take the 'middle man'as typical. Half earn less than he does, and half earn
more. Alan is the middle man. Half (50 per cent) of the other men earn less, and half earn
more than he does.
Alan's wage rate is the MEDIAN wage rate for men - £1.86 per hour.
To find the median using the cumulative percentage graph:
- Draw a horizontal line from 50 per cent across to meet the curve.
- Draw down from this point on the curve to the horizontal axis.
Read the value on the horizontal axis. This is the median.
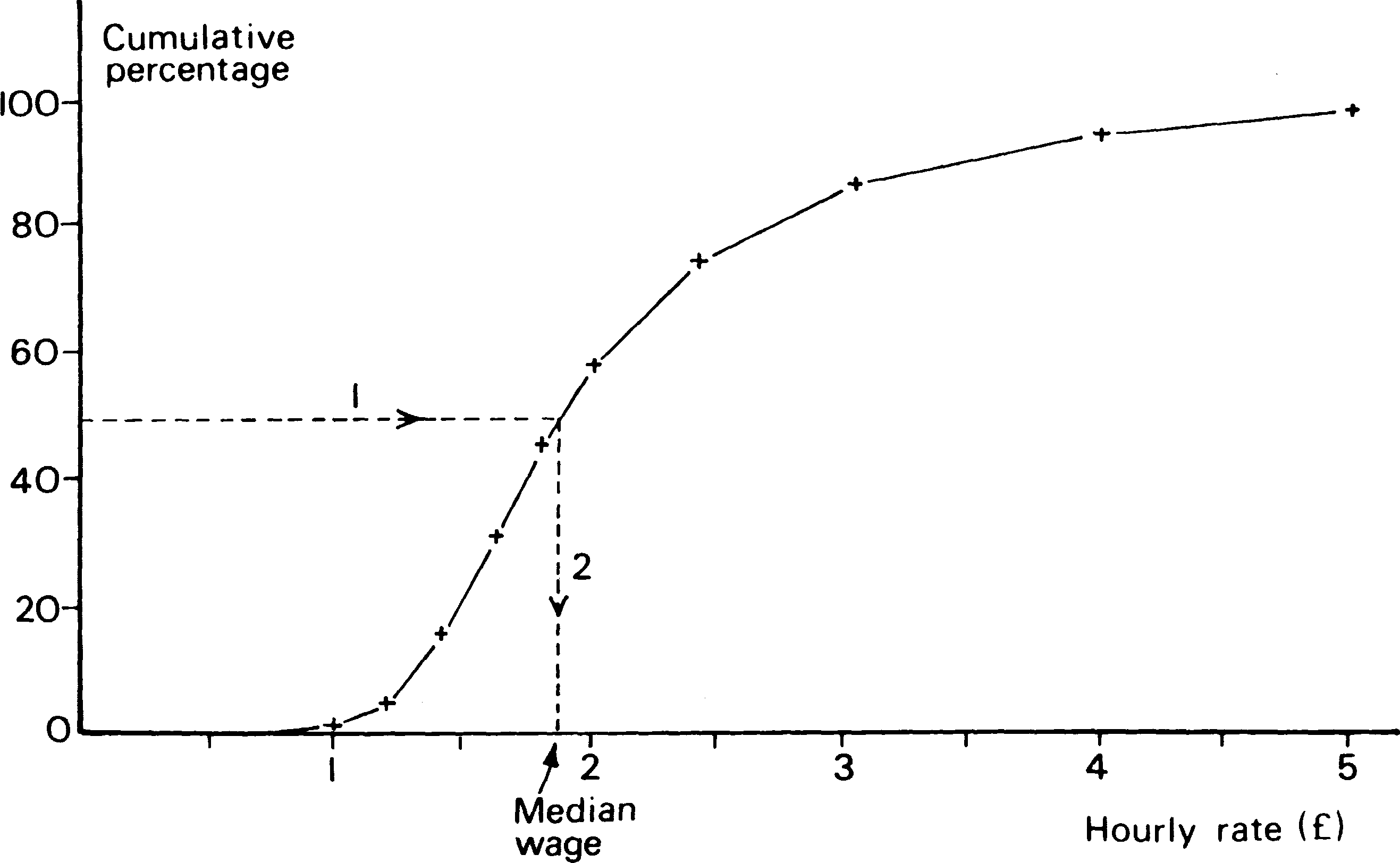
Figure 2 - Men's wage rates (April 1978). Finding the
median.
- Find the median rate of pay for women.
- How much more per hour is the median man paid than the median woman?
The cumulative percentage graph can be used to give more than the medians.
For example, the 10 per cent lowest paid men earn less than £1.30 per hour.
e,f,g,h Use your graph to find the figures that complete Table 5. (Write down
the figures only).
| |
Men |
Women |
| 10% earned less than |
130p |
96p |
| 20% earned less than |
g |
f |
| 50% earned less than |
186p |
136p |
| 80% earned less than |
g |
h |
| 90% earned less than |
317p |
224p |
Table 5 - Distribution of hourly earnings.
- *Use your answers to e and f to complete the statements:
80% of men earned more than £_____ per hour.
80% of women earned more than £_____ per hour.
Use your answers to g and h to complete the statements:
20% of men earned more than £_____ per hour.
20% of women earned more than £_____ per hour.
- The median rate for men is £1.86.What percentage of women earn more than this?
- The median rate for women is £1.36. What percentage of men earn more than this?
- How does women's pay compare with men's pay in general?
How does this show in the relative position of the two graphs?
*Comparing
Averages
In Section BI you were told the mean hourly rates for men and women.
In Section Clc you found the modal hourly rates for men and women.
In Section C4 you found the median hourly rates for men and women.
- Compare the median and mean wages for men. Why do you think the mean is more? Is the
same true for women?
The mean rate for men is higher than the median because of high wage-eamers.
- Is this true of women's pay?
- Which average do you think is fairest to use in comparing pay rates of men and women?
Try to support your choice.
|